CLOUD SERVICES
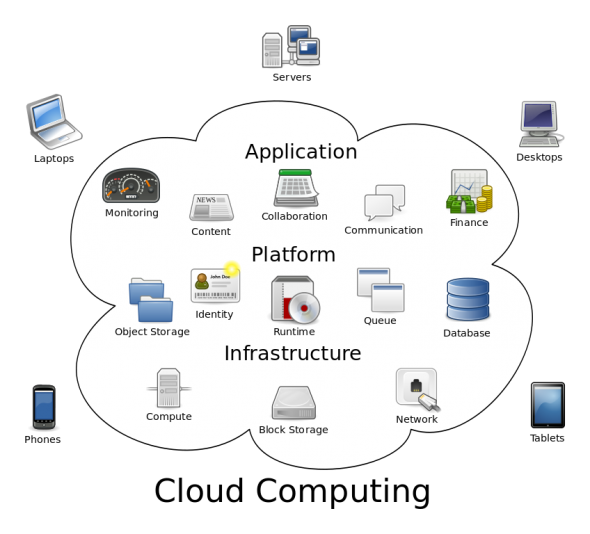
Cloud computing is the on-demand delivery of compute power, database, storage, applications, and other IT resources via the internet with pay-as-you-go pricing.
Whether you are using it to run applications that share photos to millions of mobile users or to support business critical operations, a cloud services platform provides rapid access to flexible and low cost IT resources. With cloud computing, you don’t need to make large upfront investments in hardware and spend a lot of time on the heavy lifting of managing that hardware. Instead, you can provision exactly the right type and size of computing resources you need to power your newest idea or operate your IT department. You can access as many resources as you need, almost instantly, and only pay for what you use.
Types of Clouds in Cloud Computing
Agility
The cloud allows you to innovate faster because you can focus your valuable IT resources on developing applications that differentiate your business and transform customer experiences rather than managing infrastructure and data centers. With cloud, you can quickly spin up resources as you need them, deploying hundreds or even thousands of servers in minutes.
Elasticity
Before cloud computing, you had to overprovision infrastructure to ensure you had enough capacity to handle your business operations at the peak level of activity. Now, you can provision the amount of resources that you actually need, knowing you can instantly scale up or down with the needs of your business. This reduces costs and improves your ability to meet your users’ demands.
Deploy globally in minutes
With the cloud, you can easily deploy your application in multiple physical locations around the world with just a few clicks. This means you can provide a lower latency and better experience for your customers simply and at minimal cost.
Cost savings
The cloud allows you to trade capital expense (data centers, physical servers, etc.) for variable expense and only pay for IT as you consume it. Plus, the variable expense is much lower than what you can do for yourself because of the larger economies of scale.

